വോയേജർ 2
 Model of the Voyager spacecraft design | |||||
| ദൗത്യത്തിന്റെ തരം | Planetary exploration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ഓപ്പറേറ്റർ | NASA / JPL[1] | ||||
| COSPAR ID | 1977-076A[2] | ||||
| SATCAT № | 10271[3] | ||||
| വെബ്സൈറ്റ് | voyager | ||||
| ദൗത്യദൈർഘ്യം | 46 വർഷങ്ങൾ, 8 മാസങ്ങൾ 7 ദിവസങ്ങൾ elapsed Planetary mission: 12 years, 1 month, 12 days Interstellar mission: 34 വർഷങ്ങൾ, 6 മാസങ്ങൾ 25 ദിവസങ്ങൾ elapsed (continuing) | ||||
| സ്പേസ്ക്രാഫ്റ്റിന്റെ സവിശേഷതകൾ | |||||
| നിർമ്മാതാവ് | Jet Propulsion Laboratory | ||||
| വിക്ഷേപണസമയത്തെ പിണ്ഡം | 825.5 kilograms (1,820 lb) | ||||
| ഊർജ്ജം | 470 watts (at launch) | ||||
| ദൗത്യത്തിന്റെ തുടക്കം | |||||
| വിക്ഷേപണത്തിയതി | August 20, 1977, 14:29:00 UTC | ||||
| റോക്കറ്റ് | Titan IIIE | ||||
| വിക്ഷേപണത്തറ | Cape Canaveral LC-41 | ||||
| Flyby of Jupiter | |||||
| Closest approach | July 9, 1979, 22:29:00 UTC | ||||
| Distance | 570,000 kilometers (350,000 mi) | ||||
| Flyby of Saturn | |||||
| Closest approach | August 25, 1981, 03:24:05 UTC | ||||
| Distance | 101,000 km (63,000 mi) | ||||
| Flyby of Uranus | |||||
| Closest approach | January 24, 1986, 17:59:47 UTC | ||||
| Distance | 81,500 km (50,600 mi) | ||||
| Flyby of Neptune | |||||
| Closest approach | August 25, 1989, 03:56:36 UTC | ||||
| Distance | 4,951 km (3,076 mi) | ||||
----
| |||||
1977 ഓഗസ്റ്റ് 20 ന് നാസ ബാഹ്യ ഗ്രഹങ്ങളെക്കുറിച്ച് പഠിക്കുന്ന ഒരു റോബോട്ടിക് ബഹിരാകാശ പേടകം വിക്ഷേപിച്ചു. വൊയേജർ പരിപാടിയുടെ ഭാഗമായി അതിന്റെ ജോഡി, വോയേജർ 1, വിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നതിന് 16 ദിവസം മുമ്പ് ഈ റോബോട്ടിക് ബഹിരാകാശ പേടകം വിക്ഷേപിച്ചിരുന്നു. വ്യാഴത്തിൻറെയും ശനിയുടെയും സഞ്ചാരപഥത്തിലെത്താൻ കൂടുതൽ സമയം എടുത്തു. എന്നാൽ യുറാനസ്, നെപ്റ്റ്യൂൺ എന്നിവയുമായി ആകസ്മികസമാഗമത്തിന് കൂടുതൽ സാധ്യതയുണ്ടായിരുന്നു.[4]ഈ രണ്ട് ഹിമ ഭീമൻ ഗ്രഹങ്ങളിൽ സന്ദർശിച്ചിട്ടുള്ള ഒരേയൊരു ബഹിരാകാശവാഹനമാണിത്
-
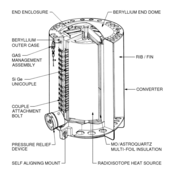
RTG inner heat source
-
RTG assembly
-
RTG unit
ഇതും കാണുക[തിരുത്തുക]
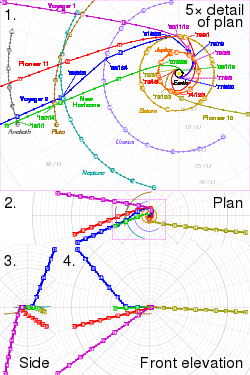
Plot 1 is viewed from the north ecliptic pole, to scale; plots 2 to 4 are third-angle projections at 20% scale.
In the SVG file, hover over a trajectory or orbit to highlight it and its associated launches and flybys.
- Family Portrait
- List of artificial objects escaping from the Solar System
- List of missions to the outer planets
- New Horizons
- Pioneer 10
- Pioneer 11
- Timeline of artificial satellites and space probes
- Voyager 1
അവലംബം[തിരുത്തുക]
Citations[തിരുത്തുക]
- ↑ "VOYAGER:Mission Information". NASA. 1989. Archived from the original on 2017-02-20. Retrieved January 2, 2011.
- ↑ "Voyager 2". US National Space Science Data Center. Retrieved August 25, 2013.[പ്രവർത്തിക്കാത്ത കണ്ണി]
- ↑ "VOYAGER 2". N2YO. Retrieved August 25, 2013.
- ↑ Butrica, Andrew. From Engineering Science to Big Science. p. 267. Retrieved September 4, 2015. "Despite the name change, Voyager remained in many ways the Grand Tour concept, though certainly not the Grand Tour (TOPS) spacecraft. Voyager 2 was launched on August 20, 1977, followed by Voyager 1 on September 5, 1977. The decision to reverse the order of launch had to do with keeping open the possibility of carrying out the Grand Tour mission to Uranus, Neptune, and beyond. Voyager 2, if boosted by the maximum performance from the Titan-Centaur, could just barely catch the old Grand Tour trajectory and encounter Uranus. Two weeks later, Voyager 1 would leave on an easier and much faster trajectory, visiting Jupiter and Saturn only. Voyager 1 would arrive at Jupiter four months ahead of Voyager 2, then arrive at Saturn nine months earlier. Hence, the second spacecraft launched was Voyager 1, not Voyager 2. The two Voyagers would arrive at Saturn nine months apart, so that if Voyager 1 failed to achieve its Saturn objectives, for whatever reason, Voyager 2 still could be retargeted to achieve them, though at the expense of any subsequent Uranus or Neptune encounter."
കൂടുതൽ വായനയ്ക്ക്[തിരുത്തുക]
- "Saturn Science Results". Voyager Science Results at Saturn. Retrieved February 8, 2005.
- "Uranus Science Results". Voyager Science Results at Uranus. Retrieved February 8, 2005.
- Nardo, Don (2002). Neptune. Thomson Gale. ISBN 0-7377-1001-2
- JPL Voyager Telecom Manual