അമോണിയം സയനൈഡ്
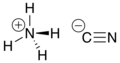
| |||
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| InChI | |||
| SMILES | |||
| Properties | |||
| തന്മാത്രാ വാക്യം | |||
| Molar mass | 0 g mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colourless crystalline solid | ||
| സാന്ദ്രത | 1.02 g/cm3 | ||
| ക്വഥനാങ്കം | |||
| very soluble | |||
| Solubility | very soluble in alcohol | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Other anions | Ammonium hydroxide Ammonium azide Ammonium nitrate | ||
| Other cations | Sodium cyanide Potassium cyanide | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
സ്ഥിരതയില്ലാത്ത ഒരു അകാർബണിക സയനൈഡ് സംയുക്തമാണ് അമോണിയം സയനൈഡ് (Ammonium cyanide). ഇതിന്റെ തന്മാത്രാ സൂത്രം NH4CN.
ഉപയോഗം[തിരുത്തുക]
കാർബണിക പദാർത്ഥങ്ങൾ നിർമ്മിക്കാനാണ് അമോണിയം സയനൈഡ് പൊതുവേ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നത്. അസ്ഥിര സംയുക്തമായതിനാൽ, വ്യവസായിക ആവശ്യങ്ങൾക്കായി കയറ്റുമതി ചെയ്യാറില്ല.
നിർമ്മാണം[തിരുത്തുക]
താഴ്ന്ന താപനിലയിൽ, ഹൈഡ്രജൻ സയനൈഡ് ജലീയ അമോണിയയുമായി ബബ്ബ്ളിംഗ് നടത്തി അമോണിയം സയനൈഡ് നിർമ്മിക്കാം
- HCN + NH3(aq) → NH4CN(aq)
കാൽസ്യം സയനൈഡ്, അമോണിയം കാർബണേറ്റ് എന്നിവ തമ്മിൽ പ്രവർത്തിപ്പിച്ചും അമോണിയം സയനൈഡ് നിർമ്മിക്കാം
- Ca(CN)2 + (NH4)2CO3 → 2 NH4CN + CaCO3
പൊട്ടാസ്യം സയനൈഡ് അല്ലെങ്കിൽ പൊട്ടാസ്യം ഫെറോസയനൈഡ് അമോണിയം ക്ലോറൈഡുമായി പ്രവർത്തിപ്പിച്ച് ലഭിക്കുന്ന വാതകം ഖരീഭവിപ്പിച്ച് അമോണിയം സയനൈഡ് ക്രിസ്റ്റൽ തയ്യാറാക്കാം.
- KCN + NH4Cl → NH4CN + KCl
രാസപ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ[തിരുത്തുക]
അമോണിയം സയനൈഡ് വിഘടിച്ച് അമോണിയ, ഹൈഡ്രജൻ സയനൈഡ് എന്നിവയുണ്ടാകുന്നു.
- [1]
- NH4CN → NH3 + HCN
ലോഹിയ ലവണങ്ങളുമായി പ്രവർത്തിക്കുന്നു. ഗ്ലയോക്സാലുമായി പ്രവർത്തിച്ച് ഗ്ലൈസീൻ (aminoacetic acid) ഉണ്ടാകുന്നു.
- NH4CN + (CHO)2 → NH2CH2COOH + HCN
വിഷം[തിരുത്തുക]
മാരക വിഷമാണ് അമോണിയം സയനൈഡ്. ശരീരത്തിലെത്തിയാൽ മരണം സംഭവിക്കാം. ലവണം വിഘടിച്ച് ഹൈഡ്രജൻ സയനൈഡ് ഉണ്ടാവുന്നതിനാൽ അതും കൈകാര്യം ചെയ്യുന്നത് അപകടമാണ്.
രാസഘടകം[തിരുത്തുക]
ഘടകങ്ങൾ: H 9.15%, C 27.23%, N 63.55%.
അവലംബം[തിരുത്തുക]
- ↑ Matthews, Clifford N (1991). "Hydrogen cyanide polymerization: A preferred cosmochemical pathway". Bioastronomy: The Search for Extraterrestrial Life—The Exploration Broadens. Lecture Notes in Physics. Vol. 390. pp. 85–87. doi:10.1007/3-540-54752-5_195. ISBN 978-3-540-54752-5.
- A. F. Wells, Structural Inorganic Chemistry, 5th ed., Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK, 1984.
| HCN | He | ||||||||||||||||||
| LiCN | Be(CN)2 | B | C | NH4CN | OCN−, -NCO |
FCN | Ne | ||||||||||||
| NaCN | Mg(CN)2 | Al(CN)3 | Si(CN)4, Me3SiCN |
P(CN)3 | SCN−, -NCS, (SCN)2, S(CN)2 |
ClCN | Ar | ||||||||||||
| KCN | Ca(CN)2 | Sc(CN)3 | Ti(CN)4 | Cr(CN)64− | Cr(CN)63− | Mn(CN)2 | Fe(CN)3, Fe(CN)64−, Fe(CN)63− |
Co(CN)2, Co(CN)3 |
Ni(CN)2 Ni(CN)42− |
CuCN | Zn(CN)2 | Ga(CN)3 | Ge | As(CN)3 | SeCN− (SeCN)2 Se(CN)2 |
BrCN | Kr | ||
| RbCN | Sr(CN)2 | Y(CN)3 | Zr(CN)4 | Nb | Mo(CN)84− | Tc | Ru(CN)63− | Rh(CN)63− | Pd(CN)2 | AgCN | Cd(CN)2 | In(CN)3 | Sn | Sb(CN)3 | Te | ICN | Xe | ||
| CsCN | Ba(CN)2 | Hf | Ta | W(CN)84− | Re | Os(CN)63− | Ir(CN)63− | Pt(CN)42-, Pt(CN)64- |
AuCN, Au(CN)2− |
Hg2(CN)2, Hg(CN)2 |
TlCN | Pb(CN)2 | Bi(CN)3 | Po | At | Rn | |||
| Fr | Ra | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |||
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||||
| La | Ce(CN)3, Ce(CN)4 |
Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd(CN)3 | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||||
| Ac | Th | Pa | UO2(CN)2 | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||||