നൈട്രിക് അമ്ലം
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Nitric acid
| |||
| Other names
Aqua fortis, Spirit of niter, Eau forte, Hydrogen nitrate, Acidum nitricum
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.832 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| Gmelin Reference | 1576 | ||
| KEGG | |||
| MeSH | {{{value}}} | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2031 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| InChI | |||
| SMILES | |||
| Properties | |||
| തന്മാത്രാ വാക്യം | |||
| Molar mass | 0 g mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless, yellow or red fuming liquid[1] | ||
| Odor | acrid, suffocating[1] | ||
| സാന്ദ്രത | 1.5129 g cm−3 | ||
| ദ്രവണാങ്കം | |||
| ക്വഥനാങ്കം | |||
| Completely miscible | |||
| log P | -0.13[2] | ||
| ബാഷ്പമർദ്ദം | 48 mmHg (20 °C)[1] | ||
| അമ്ലത്വം (pKa) | -1.4[3] | ||
| −19.9·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.397 (16.5 °C) | ||
| 2.17 ± 0.02 D | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| Std enthalpy of formation ΔfH |
−207 kJ·mol−1[4] | ||
| Standard molar entropy S |
146 J·mol−1·K−1[4] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Safety data sheet | ICSC 0183 PCTL Safety Website | ||
| EU classification | {{{value}}} | ||
| R-phrases | R8 R35 | ||
| S-phrases | (S1/2) S23 S26 S36 S45 | ||
| Flash point | {{{value}}} | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LC50 (median concentration)
|
138 ppm (rat, 30 min)[1] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 2 ppm (5 mg/m3)[1] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 2 ppm (5 mg/m3) ST 4 ppm (10 mg/m3)[1] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
25 ppm[1] | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Other anions | Nitrous acid | ||
| Other cations | Sodium nitrate Potassium nitrate Ammonium nitrate | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
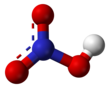
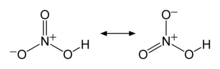
ശക്തിയേറിയ ഒരു അമ്ലമാണ് നൈട്രിക് അമ്ലം (പാക്യകാമ്ലം). രാസസമവാക്യം HNO3. ശുദ്ധ നൈട്രിക് അമ്ലത്തിന് നിറമില്ല. പഴകിയവയ്ക്ക് മഞ്ഞ നിറമുണ്ട്. നൈട്രജൻറെ ഓക്സൈഡുകളാണ് ഇതിന് കാരണം. ശക്തിയേറിയ ഓക്സീകാരീ കൂടിയാണ് നൈട്രിക് അമ്ലം. ലോഹങ്ങൾ, ഓക്സൈഡുകൾ, ഹൈഡ്രോക്സൈഡുകൾ എന്നിവയുമായി പ്രവർത്തിച്ച് നൈട്രിക് ലവണങ്ങൾ ഉണ്ടാവുന്നു. വളങ്ങൾ, സ്ഫോടകവസ്തുക്കൾ എന്നിവയുടെ നിർമ്മാണത്തിന് നൈട്രിക് അമ്ലം ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു.
ഗുണങ്ങൾ[തിരുത്തുക]
അമ്ലത്വം[തിരുത്തുക]
നൈട്രിക് അമ്ലത്തെ ഹൈഡ്രോക്ലോറിൿ അമ്ലം, സൾഫ്യൂറിൿ അമ്ലം എന്നിവയേപ്പോലെ ശക്തിയേറിയ അമ്ലമായി സാധാരണ കണക്കാക്കാറുണ്ടെങ്കിലും അതിന്റെ അമ്ലവിയോജന സ്ഥിരാങ്കം (pKa = -1.64) ഹൈഡ്രോണിയം അയോണിന്റേതിനേക്കാൾ (pKa = -1.74) കൂടുതലായതിനാൽ കൃത്യമായ നിർവചനപ്രകാരം ക്ലോറിക് അമ്ലം (HClO3), ക്രോമിക് അമ്ലം (H2CrO4), ട്രൈഫ്ലൂറൊ അസറ്റിൿ അമ്ലം(CF3COOH) എന്നിവയേപ്പോലെ നൈട്രിൿ അമ്ലവും ഒരു യഥാർഥ ശക്തിയേറിയ അമ്ലമല്ല.
ഓക്സീകരണ ഗുണങ്ങൾ[തിരുത്തുക]
ലോഹങ്ങളുമായുള്ള പ്രവർത്തനം[തിരുത്തുക]
ശക്തിയേറിയ ഓക്സീകാരീയായതു കൊണ്ട് ധാരാളം ഓർഗാനിക് വസ്തുക്കളുമായി നൈട്രിക് അമ്ലം പ്രവർത്തിക്കുന്നു. ഗാഢത, താപനില എന്നിവയനുസരിച്ച് ഉണ്ടാകുന്ന ഉല്പന്നങ്ങൾക്ക് വ്യത്യാസം ഉണ്ടാകാം. പൊതുവായ തത്ത്വം അനുസരിച്ച് ഓക്സീകരണ പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ ഗാഢ അമ്ലത്തിനൊപ്പം നടക്കുന്നു നൈട്രജൻ ഡയോക്സൈഡ് ഉണ്ടാവുന്നു(NO2).
- Cu + 4H+ + 2NO3- → Cu+2 + 2NO2 + 2H2O
അലോഹങ്ങളുമായുള്ള പ്രവർത്തനം[തിരുത്തുക]
സിലിക്കൺ, ഹാലോജനുകൾ, ഉൽകൃഷ്ടവാതകങ്ങൾ തുടങ്ങിയ അലോഹ മൂലകങ്ങളൊഴിച്ച് എല്ലാ അലോഹ മൂലകങ്ങളുമായി പ്രതിപ്രവർത്തിച്ച് അവരെ ഓക്സീകരിക്കുന്നു.
- C + 4HNO3 → CO2 + 4NO2 + 2H2O
or
- 3C + 4HNO3 → 3CO2 + 4NO + 2H2O
ഉല്പാദനം[തിരുത്തുക]
വ്യാവസായിക ഉല്പാദനം[തിരുത്തുക]
ഓക്സിജൻറെ സാനിധ്യത്തിൽ നൈട്രജൻ ഡയോക്സൈഡ് ജലവുമായി കലർത്തിയാണ് നൈട്രിക് അമ്ലം നിർമ്മിക്കുന്നത്.
ഓസ്റ്റ്വാൾഡ് പ്രക്രിയ വഴിയാണ് നൈട്രിക് അമ്ലം വ്യാവസായികമായി നിർമ്മിക്കുന്നത്.
ലബോറട്ടറി നിർമ്മാണം[തിരുത്തുക]
അവലംബം[തിരുത്തുക]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0447". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ "nitric acid_msds".
- ↑ Bell, R. P. (1973), The Proton in Chemistry (2nd ed.), Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Zumdahl, Steven S. (2009). Chemical Principles 6th Ed. Houghton Mifflin Company. p. A22. ISBN 0-618-94690-X.