നൈട്രസ് ഓക്സൈഡ്
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Dinitrogen monoxide
| |
| Other names
Laughing gas, sweet air
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.017 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1070 (compressed) 2201 (liquid) |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| InChI | |
| SMILES | |
| Properties | |
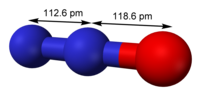
| തന്മാത്രാ വാക്യം | |
| Molar mass | 0 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless gas |
| സാന്ദ്രത | 1.977 g/L (gas) |
| ദ്രവണാങ്കം | |
| ക്വഥനാങ്കം | |
| 0.15 g/100 ml (15 °C) | |
| Solubility | soluble in alcohol, ether, sulfuric acid |
| log P | 0.35 |
| ബാഷ്പമർദ്ദം | 5150 kPa (20 °C) |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.330 |
| Structure | |
| linear, C∞v | |
| 0.166 D | |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std enthalpy of formation ΔfH |
+82.05 kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy S |
219.96 J K−1 mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| Routes of administration |
Inhalation |
| Metabolism | 0.004% |
| Elimination half-life |
5 minutes |
| Excretion | Respiratory |
| Pregnancy category |
C(US) |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | {{{value}}} |
| Related compounds | |
| Related nitrogen oxides | Nitric oxide Dinitrogen trioxide Nitrogen dioxide Dinitrogen tetroxide Dinitrogen pentoxide |
| Related compounds | Ammonium nitrate Azide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
നൈട്രജന്റെ ഒരു ഓക്സൈഡാണ് നൈട്രസ് ഓക്സൈഡ്(N
2O). ലാഫിംഗ് ഗാസ് (ചിരിപ്പിക്കുന്ന വാതകം)[1] എന്നും ഇത് അറിയപ്പെടുന്നു. ശസ്ത്രക്രിയയ്ക്കും ദന്തവൈദ്യത്തിലും അനസ്തീസിയ നൽകാൻ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു.
ചരിത്രം[തിരുത്തുക]
ഇംഗ്ലീഷ് ശാസ്ത്രജ്ഞനുമായിരുന്ന ജോസഫ് പ്രീസ്റ്റ്ലി 1772-ൽ നൈട്രസ് ഓക്സൈഡ് നിർമ്മിക്കുകയും അതിനെ ഫ്ളോജിസ്റ്റിക്കേറ്റഡ് നൈട്രസ് എയർ എന്ന് വിളിക്കുകയും ചെയ്തു.[2] പ്രീസ്റ്റ്ലി തന്റെ കണ്ടുപിടിത്തത്തെക്കുറിച്ചും നൈട്രിക് ആസിഡിനാൽ നനച്ച ഇരുമ്പ് ചൂടാക്കി നൈട്രസ് ഓക്സൈഡ് നിർമ്മിക്കുന്നതിനെക്കുറിച്ചും എക്സ്പിരിമെന്റ്സ് ആന്റ് ഒബ്സെർവേഷൻസ് ഒഫ് ഡിഫറന്റ് കൈന്റ്സ് ഒഫ് എയർ (1775) എന്ന പുസ്തകത്തിൽ വിവരിക്കുകയുണ്ടായി.[3]
ഉപയോഗങ്ങൾ[തിരുത്തുക]
ഫുഡ് എയറോസോളുകളിൽ ഈ വാതകം ഒരു പ്രൊപ്പല്ലന്റായി ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു.ഓട്ടോമൊബൈൽ റേസിംഗിൽ, ഒരു എഞ്ചിന്റെ വായു ഉപഭോഗത്തിലേക്ക് നൈട്രസ് ഓക്സൈഡ് കുത്തിവയ്ക്കുന്നു;അധിക ഓക്സിജൻ ഒരു സ്ട്രോക്കിന് കൂടുതൽ ഇന്ധനം കത്തിക്കാൻ എഞ്ചിനെ അനുവദിക്കുന്നു.നൈട്രിക് ആസിഡിലെ സിങ്കിന്റെ പ്രവർത്തനത്തിലൂടെയും സോഡിയം നൈട്രൈറ്റിലെ (NaNO2) ഹൈഡ്രോക്സൈലാമൈൻ ഹൈഡ്രോക്ലോറൈഡിന്റെ (NH2OH · HCl) പ്രവർത്തനത്തിലൂടെയും ഇത് തയ്യാറാക്കപ്പെടുന്നു.
അവലംബം[തിരുത്തുക]
- ↑ Tarendash, Albert S. (2001). Let's review: chemistry, the physical setting (3rd ed.). Barron's Educational Series. p. 44. ISBN 0-7641-1664-9., Extract of page 44
- ↑ Keys TE (1941). "The_Development_of_Anesthesia". American Scientist. 2: 552–574. Bibcode:1982AmSci..70..522D. Archived from the original on 2014-01-12. Retrieved 2013-03-04.
{{cite journal}}: More than one of|work=and|journal=specified (help) - ↑ Priestley J (1776). "Experiments and Observations on Different Kinds of Air (vol.2, sec.3)".
- CS1 errors: redundant parameter
- Chemical articles with multiple compound IDs
- Multiple chemicals in an infobox that need indexing
- Pages using Chembox with unknown parameters
- Articles with changed EBI identifier
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Chembox
- Chembox image size set
- രസതന്ത്രം - അപൂർണ്ണലേഖനങ്ങൾ
- ഓക്സൈഡുകൾ
- ഹരിതഗൃഹ വാതകങ്ങൾ

