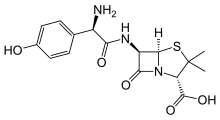
അമോക്സിലിൻ
 | |
 | |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
(2S,5R,6R)-6-{[(2R)-2-amino-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-acetyl]amino}-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-24-carboxylic acid | |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Amoxil, Tycil, Trimox, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a685001 |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | Oral, intravenous |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 95% oral |
| Metabolism | less than 30% biotransformed in liver |
| Biological half-life | 61.3 minutes |
| Excretion | renal |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 26787-78-0 |
| ATC code | J01CA04 (WHO) QG51AA03 |
| PubChem | CID 33613 |
| DrugBank | DB01060 |
| ChemSpider | 31006 |
| UNII | 9EM05410Q9 |
| KEGG | D07452 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:2676 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1082 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C16H19N3O5S |
| Molar mass | 365.4 g/mol |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
അമോക്സിലിൻ ബാക്ടീരിയ ബാധമൂലമുണ്ടാകുന്ന രോഗങ്ങളെ ചികിത്സിക്കാൻ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്ന ആന്റിബയോട്ടിക്ക് ആണ്[1]. മദ്ധ്യകർണ്ണത്തിൽ ബാധിക്കുന്ന അണുബാധയ്ക്കായി ഇതു ഉപയോഗിച്ചുവരുന്നു. തൊണ്ടയിലെ സ്ട്രെപ്റ്റോക്കോക്കസ് അണുബാധ, ന്യൂമോണിയ, ത്വക്കിലെ അണുബാധ, മൂത്രാശയാണുബാധ തുടങ്ങിയവയ്ക്കും ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു. വായിലൂടെയാണ് ഇതു അകത്തെയ്ക്ക് കഴിക്കുന്നത്.[1] ഓക്കാനം, തടിപ്പ് എന്നീ സാധാരണ സൈഡ് എഫക്ടുകൾ ഉണ്ടാകാറുണ്ട്.[1] നാവിലും മറ്റും ഉണ്ടാകുന്ന പൂപ്പൽ ബാധ കൂടാനും ക്ലാവുലാനിക് ആസിഡിന്റെ കൂടെ ഉപയോഗിച്ചാൽ വയറിളക്കവും ഉണ്ടാകാം[2]. പെനിസില്ലിൻ അലർജ്ജിയുള്ളവർക്ക് ഇത് നൽകാൻ പാടില്ല. കിഡ്നി രോഗമുള്ളവർക്ക് അമോക്സിലിൻ കുറഞ്ഞ അളവിലേ നൽകാവു. എന്നാൽ ഗർഭാവസ്ഥയിലും മുലയൂട്ടുന്ന സമയത്തും ഇതു നൽകിയാൽ കുഴപ്പമില്ല എന്നു തെളിഞ്ഞിട്ടുണ്ട്.[1]
1972ൽ ആണ് അമോക്സിലിൻ ആദ്യമായി കിട്ടിത്തുടങ്ങിയത്. [3]അമോക്സിലിൻ ലോകാരോഗ്യസംഘടനയുടെ അടിസ്ഥാന ആരോഗ്യമേഖലയിൽ വേണ്ട അവശ്യമരുന്നുകളുടെ പട്ടികയിൽ ഏറ്റവും പ്രമുഖമായ സ്ഥാനമുള്ള, ഔഷധമാണ്. [4]കുട്ടികൾക്ക് ഡോക്ടർമാർ സാധാരണ എഴുതിക്കൊടുക്കുന്ന ആന്റിബയോട്ടിക്കുകളിൽ ഒന്നാണിത്.[5] ജെനറിക് ഔഷധങ്ങളിൽ ഒന്നായി അമോക്സിലിനും ചേർത്തിട്ടുണ്ട്.[1] വികസിതരാജ്യങ്ങളിൽ വളരെ ചെലവുകുറഞ്ഞ് ലഭിക്കുന്ന ഈ ഔഷധത്തിന് [6]യു എസ് പോലുള്ള രാജ്യങ്ങളിൽ വില കൂടുതലാണ്. [1]
വൈദ്യശാസ്ത്രരംഗത്തെ ഉപയോഗങ്ങൾ[തിരുത്തുക]

അമോക്സിലിൻ അനേകം തരം അണുബാധകൾക്ക് ചികിത്സയ്ക്കായി ഉപയോഗിച്ചുവരുന്നു. ന്യൂമോണിയ, സ്ട്രെപ്റ്റൊകോക്കൽ ഫാറിംഗൈറ്റിസ്, മൂത്രാശയരോഗങ്ങൾ, സാൽമണെല്ല അണുബാധകൾ, ലൈം ഡിസീസ്, ക്ലാമീഡിയ അണുബാധ തുടങ്ങിയവയ്ക്കും ഉപയോഗിച്ചുവരുന്നു. [1]
ശ്വാസകോശ അണുബാധ[തിരുത്തുക]
സൈനസൈറ്റിസിനു കാരണമായ ബാക്ടീരിയയെ നശിപ്പിക്കാൻ അമോക്സിലിനും അമോക്സിലിൻ - ക്ലാവുലനേറ്റ് സംയുക്തവും ഉപയോഗിച്ചുവരുന്നു. എന്നാൽ കൂടുതൽ സൈനസൈറ്റിസും വൈറസ് മൂലമായതിനാൽ അമോക്സിലിനും അമോക്സിലിൻ - ക്ലാവുലനേറ്റ് സംയുക്തവും ഫലപ്രദമല്ല.[7] ഇക്കാര്യത്തിൽ ചെറിയ ഗുണം അമോക്സിലിൻ ഉപയൊഗിക്കുന്നതിലുണ്ടായാലും അതിന്റെ വിപരീതഗുണം കൂടുതൽ സ്പഷ്ടമായിരിക്കും. [8]
ത്വക്ക് അണുബാധകൾക്ക്[തിരുത്തുക]
അമോക്സിലിൻ ത്വക്ക് രോഗമായ, ആഗ്നി വൾഗാരിസ് തുടങ്ങിയവയ്ക്കു ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു. [9] മറ്റു ഔഷധങ്ങളുമായി പ്രതികരിക്കാത്ത ചില അണുബാധകൾക്കെതിരെയും അമോക്സിലിൻ ഫലപ്രദമാണ്. [10]
-
Nonallergic amoxicillin rash eight days after first dose: This photo was taken 24 hours after the rash began.
-
Eight hours after the first photo, individual spots have grown and begun to merge.
-
At 23 hours after the first photo, the color appears to be fading, and much of rash has spread to confluence.
പ്രതിപ്രവർത്തനം[തിരുത്തുക]
അമോക്സിലിൻ താഴെപ്പറയുന്ന ഔഷധങ്ങളോട് പ്രതികരിച്ചേയ്ക്കാം:
- Anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin, dabigatran)[11]
- Allopurinol (gout treatment)
- ചില ആന്റിബയോട്ടിക്കുകളുമായി
- കാൻസർ ചികിത്സ (methotrexate)
- Uricosuric drugs
- ടൈഫോയിഡ് വാക്സിൻ
പ്രവർത്തനരീതി[തിരുത്തുക]
ചരിത്രം[തിരുത്തുക]
സമൂഹവും സംസ്കാരവും[തിരുത്തുക]
ഉപയോഗക്രമം[തിരുത്തുക]
പേരുകൾ[തിരുത്തുക]
അവലംബം[തിരുത്തുക]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 "Amoxicillin". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 1 August 2015.
- ↑ Gillies, M; Ranakusuma, A; Hoffmann, T; Thorning, S; McGuire, T; Glasziou, P; Del Mar, C (17 November 2014). "Common harms from amoxicillin: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials for any indication". CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association [Journal de l'Association medicale canadienne]. 187: E21-31. doi:10.1503/cmaj.140848. PMID 25404399.
- ↑ Roy, Jiben (2012). An introduction to pharmaceutical sciences production, chemistry, techniques and technology. Cambridge: Woodhead Pub. p. 239. ISBN 9781908818041.
- ↑ "19th WHO Model List of Essential Medicines" (PDF). World Health Organization. April 2015. Retrieved 14 December 2015.
- ↑ Kelly, Deirdre (2008). Diseases of the liver and biliary system in children (3 ed.). Chichester, UK: Wiley-Blackwell. p. 217. ISBN 9781444300543.
- ↑ "Amoxicillin". International Drug Price Indicator Guide. Retrieved 1 August 2015.[പ്രവർത്തിക്കാത്ത കണ്ണി]
- ↑ "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question" (PDF). Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation. American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-11-03. Retrieved August 14, 2012.
{{cite journal}}: Cite uses deprecated parameter|authors=(help) - ↑ Ahovuo-Saloranta, A.; Rautakorpi, U. M.; Borisenko, O. V.; Liira, H.; Williams Jr, J. W.; Mäkelä, M. (2014). Ahovuo-Saloranta, Anneli (ed.). "Antibiotics for acute maxillary sinusitis". The Cochrane Library. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000243.pub3.
- ↑ "Adolescent Acne: Management".
- ↑ "Amoxicillin and Acne Vulgaris". scienceofacne.com. 2012-09-05. Archived from the original on 2012-07-21. Retrieved 2012-08-17.
- ↑ British National Formulary 57 March 2009
കൂടുതൽ വായനയ്ക്ക്[തിരുത്തുക]
- Neal, M. J. (2002). Medical pharmacology at a glance (4th ed.). Oxford: Blackwell Science. ISBN 0-632-05244-9.
- British National Formulary 45 March 2003