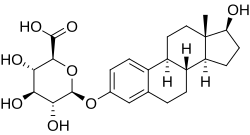
എസ്ട്രാഡൈയോൾ 3-ഗ്ലൂക്കുറോണൈഡ്
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2S,3S,4S,5R,6S)-3,4,5-Trihydroxy-6-{[(1S,3aS,3bR,9bS,11aS)-1-hydroxy-11a-methyl-2,3,3a,3b,4,5,9b,10,11,11a-decahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-7-yl]oxy}oxane-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
E2-3G; 17β-Estradiol 3-(β-D-glucuronide); 17β-Hydroxyestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-3-yl β-D-glucopyranosiduronic acid;
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| InChI | |
| SMILES | |
| Properties | |
| തന്മാത്രാ വാക്യം | |
| Molar mass | 0 g mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
എസ്ട്രാഡൈയോൾ 3-ഗ്ലൂക്കുറോണൈഡ് (ഇ2-3ജി), Estradiol 3-glucuronide (E2-3G)17ബീറ്റ-എസ്റ്റ്രാഡയോൽ 3-(ബീറ്റ-ഡി-ഗ്ലൂക്കുറോണൈഡ്)17β-estradiol 3-(β-D-glucuronide) എന്നും അറിയപ്പെടുന്നു, ഇത് സ്വാഭാവികമായും ശരീരത്തിൽ ഉണ്ടാകുന്ന ഈസ്ട്രജൻ രാസസംയുക്തമാണ്.[1] ശരീരത്തിലെ പ്രധാന ഈസ്ട്രജനായ എസ്ട്രാഡിയോളിന്റെ C3 ഗ്ലൂക്കുറോണൈഡ് സംയോജനമാണ് ഇത്.[1] ഇത് ഗ്ലൂക്കുറോണിക് ആസിഡിന്റെ ചേർച്ച വഴി യുഡിപി-ഗ്ലൂക്കുറോനോസൈൽട്രാൻസ്ഫെറേസ് വഴി കരളിലെ എസ്ട്രാഡിയോളിൽ നിന്ന് രൂപപ്പെടുകയും ഒടുവിൽ മൂത്രത്തിലും പിത്തരസത്തിലും പുറന്തള്ളപ്പെടുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു.[2] [3]ഈസ്ട്രോൺ സൾഫേറ്റ് പോലെയുള്ള ഈസ്ട്രജൻ സൾഫേറ്റുകൾക്ക് സമാനമായി, ഈസ്ട്രജൻ ഗ്ലൂക്കുറോണൈഡുകൾക്ക് എസ്ട്രാഡിയോൾ പോലെയുള്ള സംയോജിത ഈസ്ട്രജനുകളേക്കാൾ വളരെ ഉയർന്നതോതിൽ വെള്ളത്തിൽ ലയിക്കാനുള്ള ശേഷിയുണ്ട്.[3]
സസ്തനഗ്രന്ഥി പോലുള്ള ഈ എൻസൈം പ്രകടിപ്പിക്കുന്ന കോശങ്ങളിലെ β- ഗ്ലൂക്കുറോണിഡേസ് വഴി ഈസ്ട്രജൻ ഗ്ലൂക്കുറോണൈഡുകളെ അനുബന്ധ സ്വതന്ത്ര ഈസ്ട്രജനുകളിലേക്ക് ഡീകോൻജുഗേറ്റ് ചെയ്യാൻ കഴിയും.[2] തൽഫലമായി, ഈസ്ട്രജൻ ഗ്ലൂക്കുറോണൈഡുകൾ ഈസ്ട്രജൻ ആയി പരിവർത്തനം ചെയ്യുന്നതിലൂടെ ഈസ്ട്രജനിക് പ്രവർത്തനം നടത്തുന്നു.
ഇതും കാണുക[തിരുത്തുക]
- കാറ്റെക്കോൾ ഈസ്റ്റ്രജൻ (Catechol estrogen )
- ഈസ്റ്റ്രഡയോൾ സൾഫേറ്റ് (Estradiol sulfate)
- ഈസ്രയോൾ ഗ്ലൂക്കുറോണൈഡ് (Estriol glucuronide)
- എസ്ട്രയോൾ സൽഫേറ്റ് (Estriol sulfate )
- ഈസ്റ്റ്രജൻ കോൺജുഗേറ്റ് (Estrogen conjugate)
- ലിപോയ്ഡൽ എസ്റ്റ്രാഡയോൾ (Lipoidal estradiol)
റഫറൻസുകൾ[തിരുത്തുക]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Human Metabolome Database: Showing metabocard for 17-beta-Estradiol-3-glucuronide (HMDB0006224)".
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Zhu BT, Conney AH (January 1998). "Functional role of estrogen metabolism in target cells: review and perspectives". Carcinogenesis. 19 (1): 1–27. doi:10.1093/carcin/19.1.1. PMID 9472688.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Kuhl H (2005). "Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration" (PDF). Climacteric. 8 Suppl 1: 3–63. doi:10.1080/13697130500148875. PMID 16112947. S2CID 24616324.
