ലോഗരിതം
| Arithmetic operations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

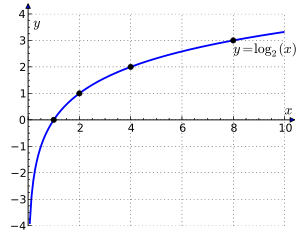
ഒരു ആധാരസംഖ്യയുടെ എത്രാമത് ഘാതമാണ് നിർദ്ദിഷ്ടസംഖ്യ എന്ന് കാണിക്കുന്ന സംഖ്യ അതായത് ഘാതാങ്കം ആണ് ലോഗരിതം. m എന്ന സംഖ്യയെ an എന്ന രൂപത്തിലെഴുതിയാൽ a ആധാരവും n, m-ന്റെ ലോഗരിതവും ആണ്.
പൂർണ്ണസംഖ്യയും ദശാംശസംഖ്യയും ചേർന്നതാണ് ലോഗരിതം. പൂർണ്ണസംഖ്യയെ പൂർണ്ണാംശം എന്നും ദശാംശസംഖ്യയെ ഭിന്നാംശം എന്നും വിളിക്കുന്നു. ഉദാഹരണത്തിന് 2.345 എന്നതിൽ 2 പൂർണ്ണാംശവും 0.345എന്നത് ഭിന്നാംശവും ആണ്.
രണ്ട് തരം ലോഗരിതങ്ങൾ ഉപയോഗത്തിലുണ്ട്.
- സാധാരണ ലോഗരിതം(Common logarithm) അഥവാ ബ്രിഗ് ലോഗരിതം. 10 ആധാരമായ ലോഗരിതമാണ് സാധാരണ ലോഗരിതം. ഇതിനെ log എന്നാണ് സൂചിപ്പിക്കുന്നത്.
- സ്വാഭാവിക ലോഗരിതം(Natural logarithm) അഥവാ നേപിയർ ലോഗരിതം. e ആധാരമായ ലോഗരിതമാണ് സ്വാഭാവിക ലോഗരിതം. ഇതിനെ loge എന്നോ ln എന്നോ സൂചിപ്പിക്കുന്നു.
അവലംബം[തിരുത്തുക]
ഹൈസ്കൂൾ ശാസ്ത്രനിഘണ്ടു,കേരള ശാസ്ത്രസാഹിത്യപരിഷത്ത് പ്രസിദ്ധീകരണം











![{\displaystyle \scriptstyle {\sqrt[{\text{degree}}]{\scriptstyle {\text{radicand}}}}\,=\,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5582d567e7e7fbcdb728291770905e09beb0ea18)


