സിൽവർ ബ്രോമൈഡ്
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Other names | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.160 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| InChI | |||
| SMILES | |||
| Properties | |||
| തന്മാത്രാ വാക്യം | |||
| Molar mass | 0 g mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Pale yellow solid photosensitive | ||
| സാന്ദ്രത | 6.473 g/cm3, solid | ||
| ദ്രവണാങ്കം | |||
| ക്വഥനാങ്കം | |||
| 0.140 mg/L (20 °C) | |||
Solubility product (Ksp)
|
5.4 × 10 −13 | ||
| Solubility | insoluble in alcohol, most acids sparingly soluble in ammonia soluble in alkali cyanide solutions | ||
| Band gap | 2.5 eV | ||
| Electron mobility | 4000 cm2/(V·s) | ||
| −59.7·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Refractive index (nD) | 2.253 | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| Std enthalpy of formation ΔfH |
−100 kJ·mol−1[1] | ||
| Standard molar entropy S |
107 J·mol−1·K−1[1] | ||
| Specific heat capacity, C | 270 J/(kg·K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Other anions | Silver(I) fluoride Silver chloride Silver iodide | ||
| Other cations | Copper(I) bromide Mercury(I) bromide | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
വെള്ളിയുടെ ഒരു ഹാലൈഡാണ് സിൽവർ ബ്രോമൈഡ്. മഞ്ഞ നിറത്തോടു കൂടിയ ഈ മൃദുലവണം ജലത്തിൽ അലേയമാണ്. പ്രകാശത്തോടുള്ള ഈ സംയുക്തത്തിന്റെ പ്രതികരണം, ഫോട്ടോഗ്രാഫിയിൽ പ്രയോജനപ്പെടുന്നു.
സാന്നിദ്ധ്യം[തിരുത്തുക]
ബ്രോമാർജിറൈറ്റ് എന്ന ധാതു രൂപത്തിൽ സിൽവർ ബ്രോമൈഡ് പ്രകൃതിയിൽ കാണപ്പെടുന്നു.
തയ്യാറാക്കൽ[തിരുത്തുക]
ധാതുരൂപത്തിൽത്തന്നെ സിൽവർ ബ്രോമൈഡ് കാണപ്പെടുന്നുവെങ്കിലും സിൽവർ നൈട്രേറ്റ് ഒരു ആൽക്കലി ബ്രോമൈഡുമായി പ്രവർത്തിപ്പിച്ചാണ് ഇതിന്റെ വ്യവസായിക ഉൽപാദനം നടത്തുന്നത്. പൊട്ടാസ്യം ബ്രോമൈഡ് ആണ് സാധാരണയായി ഉപയോഗിക്കാറുള്ളത്. ധാതുവിൽ നിന്നും നേരിട്ടും നിർമ്മാണം നടത്താറുണ്ട്.
രാസപ്രവർത്തനം[തിരുത്തുക]
സിൽവർ ബ്രോമൈഡ് ജലീയ അമോണിയയുമായി പ്രവർത്തിച്ച് വിവിധ അമീനുകൾ ഉണ്ടാവുന്നു. [2]
AgBr + nNH3 → Ag(NH3)21+
- {AgBr(NH3)2}
{AgBr2(NH3)2}1−
{AgBr(NH3)}
{AgBr2(NH3)}1−
- {AgBr(NH3)2}
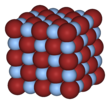
ക്രിസ്റ്റൽ ഘടന[തിരുത്തുക]
സിൽവർ ഫ്ലൂറൈഡ്, സിൽവർ ക്ലോറൈഡ്, സിൽവർ ബ്രോമൈഡ് എന്നിവയെല്ലാം ക്യുബിക് ഘടനയുള്ളവയാണ്. [3]
ലേയത്വം[തിരുത്തുക]
സിൽവർ ബ്രോമൈഡിന്റെ ലേയത്വം സിൽവർ ഫ്ലൂറൈഡിനെ അപേക്ഷിച്ച് വളരെക്കുറവാണ്. എന്നാൽ സിൽവർ അയോഡൈഡിനെക്കാളും തവണ കൂടുതലാണ്. [4]
| Compound | Solubility (g / 100 g H2O) |
| AgF | 172 |
| AgCl | 0.00019 |
| AgBr | 0.000014 |
| AgI | 0.000003 |
പ്രകാശ പ്രതികരണം[തിരുത്തുക]
അവലംബം[തിരുത്തുക]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Zumdahl, Steven S. (2009). Chemical Principles 6th Ed. Houghton Mifflin Company. p. A23. ISBN 978-0-618-94690-7.
- ↑ Leden, I., Persson, G.; Persson; Sjöberg; Dam; Sjöberg; Toft (1961). "The Solubility of Silver Chloride and Silver Bromide in Aqueous Ammonia and the Formation of Mixed Silver-Ammonia-Halide Complexes". Acta Chem. Scand. 15: 607–614. doi:10.3891/acta.chem.scand.15-0607.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Glaus, S.; Calzaferri, G. (2003). "The band structures of the silver halides AgF, AgCl, and AgBr: A comparative study". Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2 (4): 398–401. doi:10.1039/b211678b.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ↑ Lide, David R. (ed). (2005)Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 86th Edition, The Chemical Rubber Publishing Co., Cleveland.